Print Logs Without Code Change in Android
While developing an application, you need to check if it works as you expected. Typical points to check are variable values and method calls. For that, you can add some logs and verify whether a value is correct or a method is called. In Android, Log class provides logging with different levels (e.g. error, warn, info, debug).
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.d(TAG, String.format("onCreate, savedInstanceState=%s", savedInstanceState));
...
}This works quite well but it has some drawbacks. First of all, you need to modify your code. Then, you should remove that code if you added it just for verifying some logic. It would be okay if you check a few places. However, it would be cumbersome if you need to add logging to multiple places.
Adding breakpoints could be a good alternative than logging. In Android Studio, you can add a breakpoint by clicking a gutter next to the line number. The red circle appears and indicates that a breakpoint is enabled.
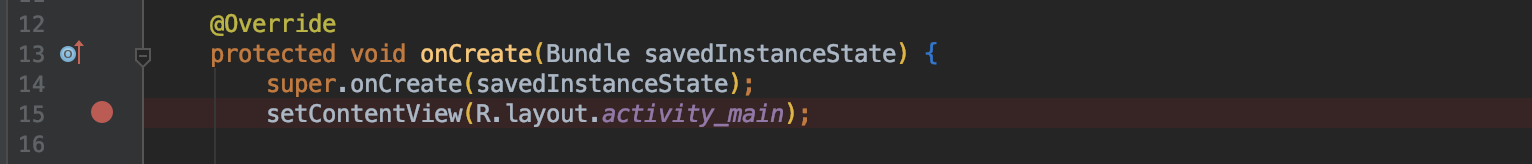
When you launch your application with a debugger, your app will be suspended at that line and you can check variables.
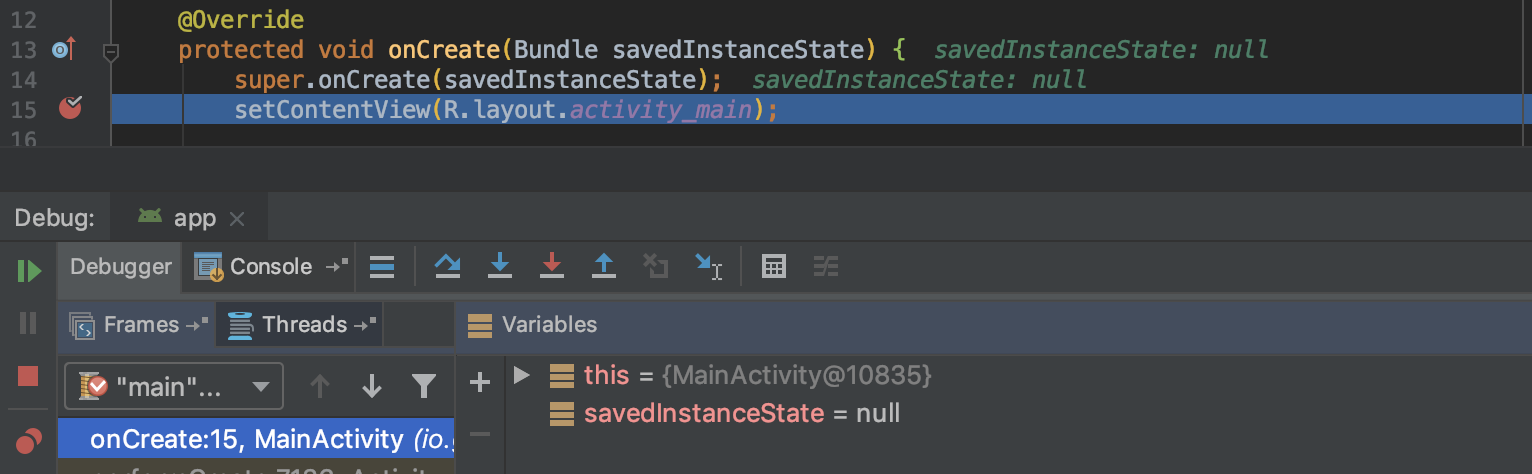
Breakpoints allow you to check method calls and variables without changing your code. This is quite handy but sometimes it doesn’t work well because of suspension. Scroll events or touch events are continuous events. If the application is suspended to check values, the continuity is broken and the logic could act differently. For example, the double-tap event might not be triggered if the application is suspended for a long time on the first tap.
You could consider again on cumbersome logging code for those cases. Fortunately, Android Studio supports breakpoints with more advanced options. With that, you can print logs without suspension. To see those options, click on More after right-clicking on the breakpoint. Or, click the menu on Run > View Breakpoints....
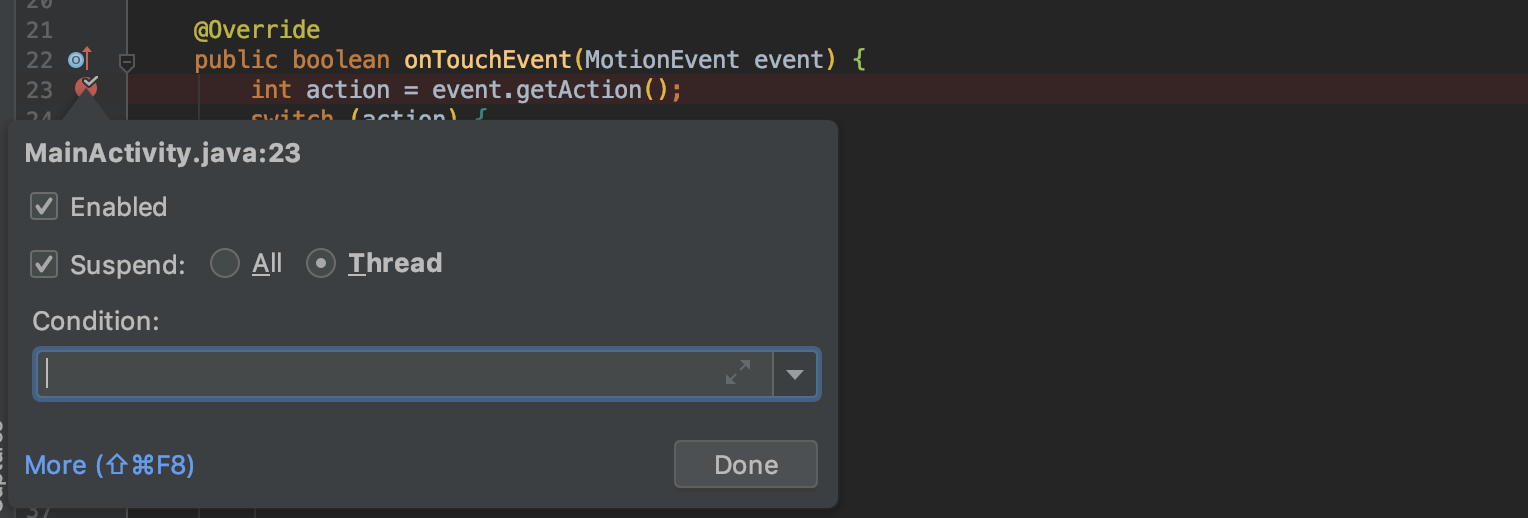
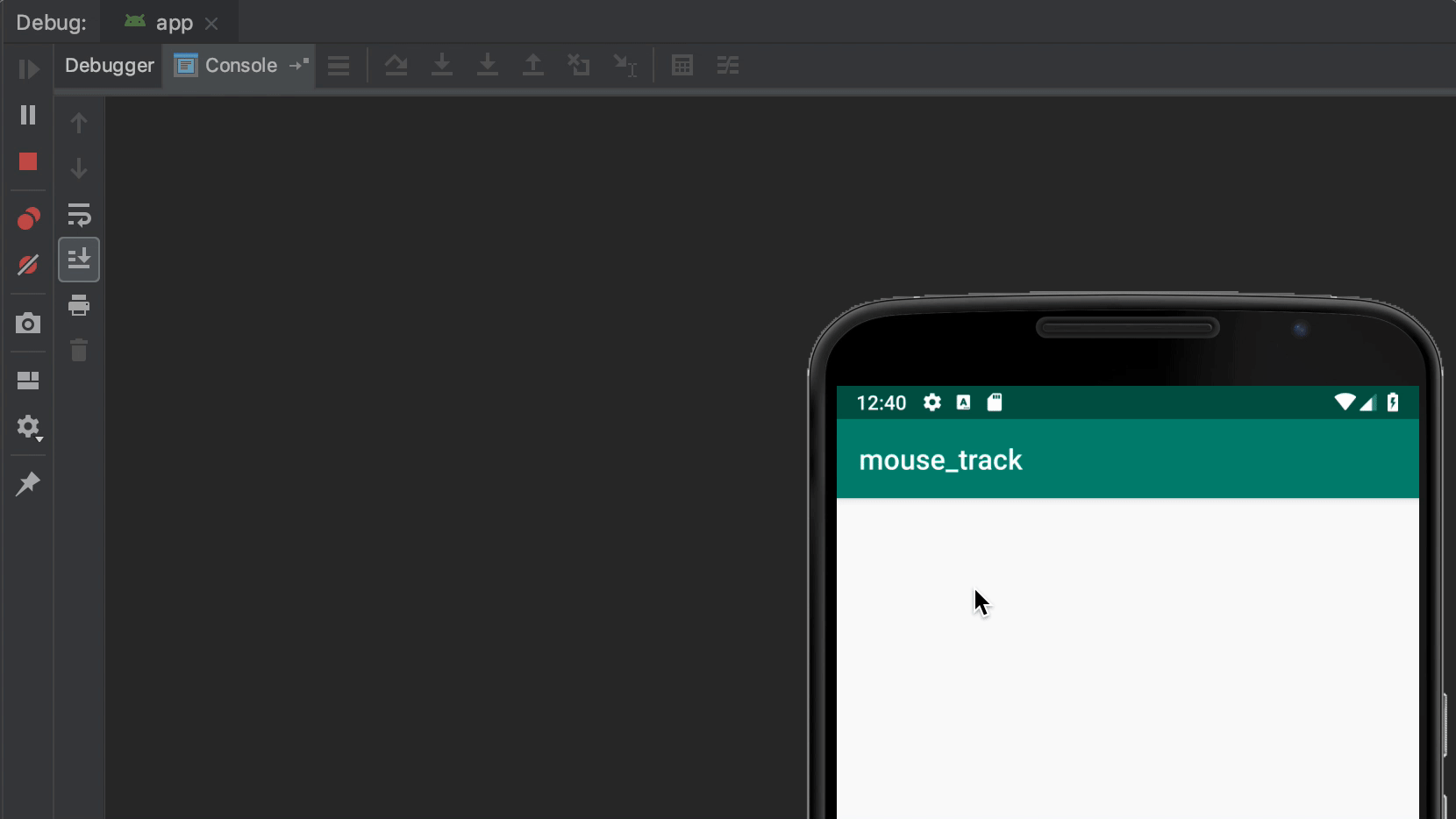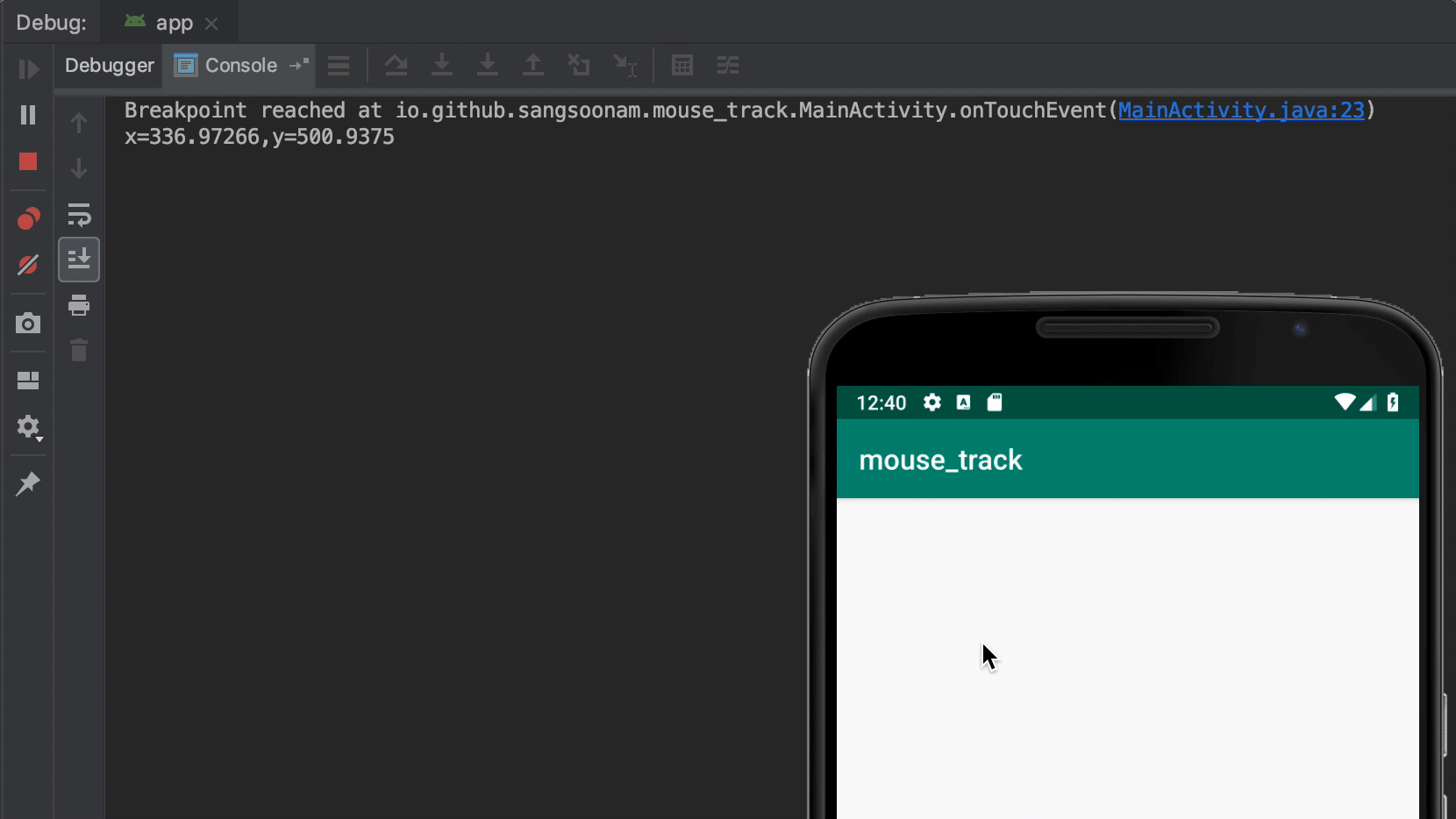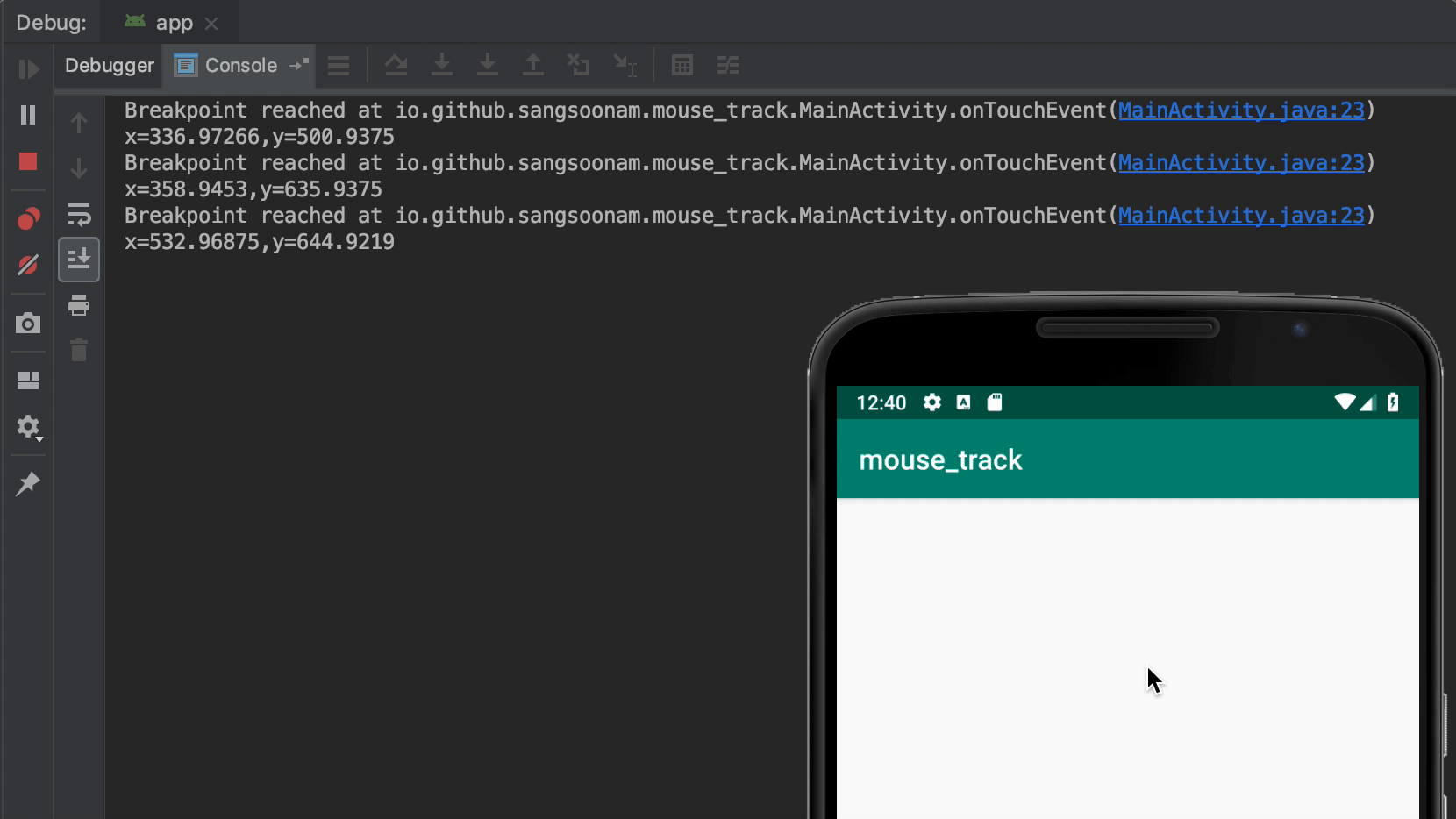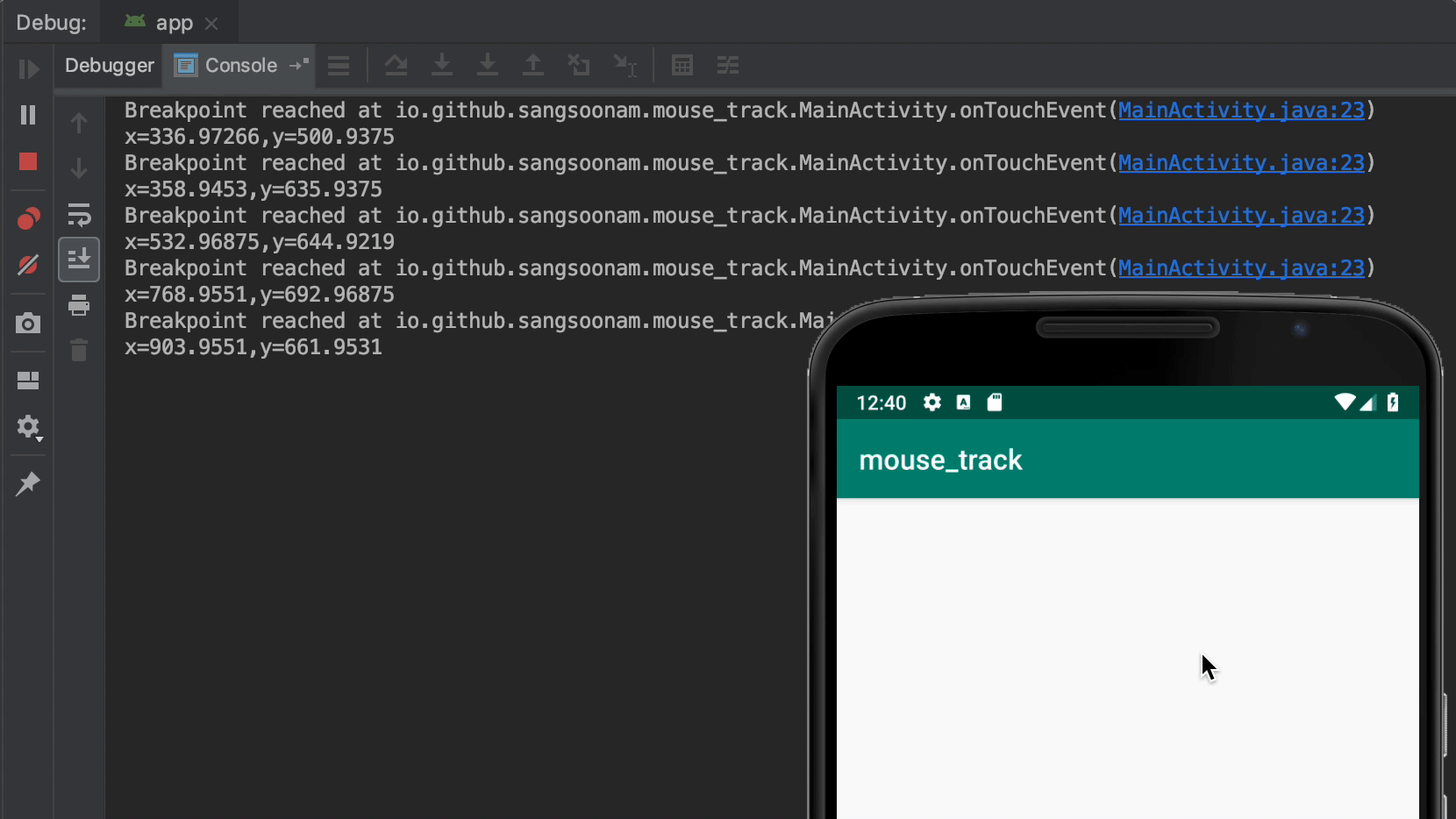
In the popup, the first thing to do is unselect Suspend. Then, you can configure how to print logs. Breakpoint hit message is a simple way to print logs if that line is called. You can also customize a log message with available variables at that line. Lastly, Condition does filtering to trigger logging only when it matches.
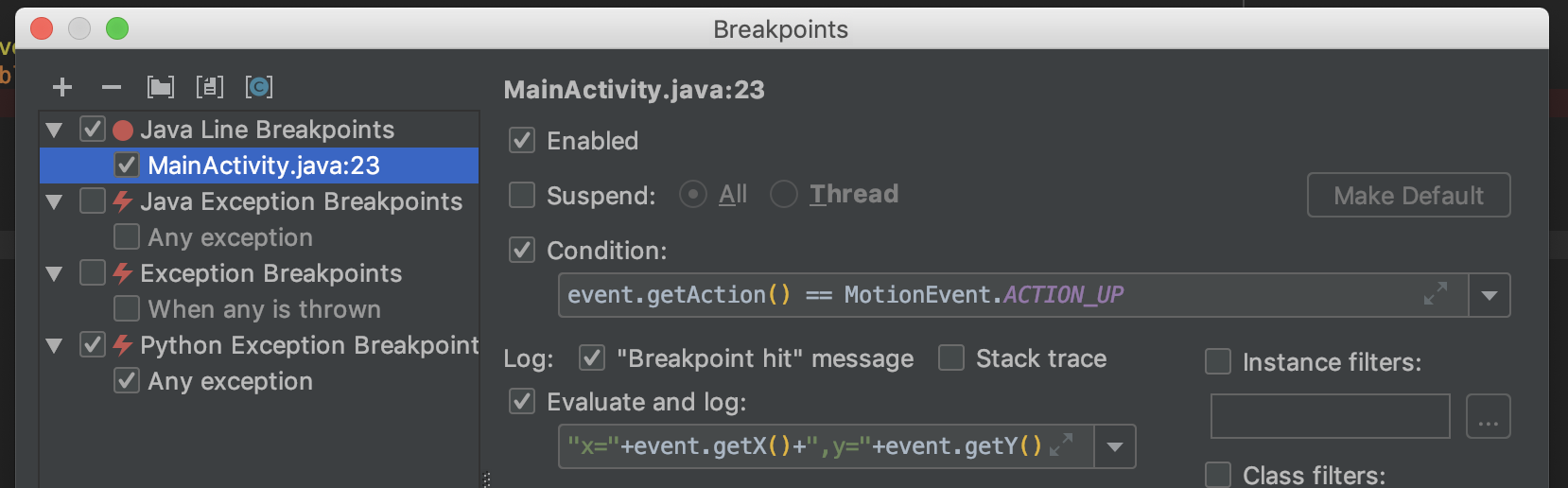
When you use Log class for logging, you check logs in the Logcat tab. Whereas, breakpoint logs appear in Debug > Console tab. This is because it works only with a debugger and doesn’t use Log class.
Conclusion
If you want to print logs for debugging purpose, you can use breakpoint logs supported by Android Studio. You can customize a log message without modifying any code. Furthermore, it is even suitable for continuous events such as scrolling or touching by unselecting Suspend option.